Few days back, I decided to setup development environment for deep learning on my Windows 10 laptop. In this article, I would share my experience in setting up a system typically for Data Science developers. Although I used Windows 10 but the steps will be same for Linux and Mac OS.
Jupyter Extension for Visual Studio Code A Visual Studio Code extension that provides basic notebook support for language kernels that are supported in Jupyter Notebooks today. Many language kernels will work with no modification. To enable advanced features, modifications may be needed in the VS Code language extensions. Follow me on twitter: depth tutorial about how to get and open jupyter notebook inside visual studio code.
Being a developer, need IDE for coding and not fan of browser based editor. Jupyter Notebook is favourite tool for data scientist and we can’t skip that in case of data science. Fortunately, VS Code supports Jupyter notebook. You can now directly edit .ipynb files and get the interactivity of Jupyter notebooks with all of the power of VS Code. We will go through it.
In this tutorial, we will cover the following steps:
1. Install Python
2. Install TensorFlow 2.0
3. Install Jupyter Notebook
4. Setup VS Code
5. Testing Environment
6. Virtual Environment (Optional)
1. Install Python
Download Python 3.7.6 from www.python.org(Currently, Tensorflow doesn’t support Python 3.8). I would suggest to install it with “customize installation” option and allow all users.
After installation, check the Python version on terminal. If there are multiple versions of python installed in the machine then change PATH in environment variable to the installed version and restart terminal to check version.
2. Install TensorFlow 2.0
TensorFlow is open source deep learning framework by Google, helps us to build and design Deep Learning models.
For simplicity, we will install CPU version of TensorFlow.
It will install all supportive extensions like numpy …etc.

Note: Install the GPU version of TensorFlow only if you have an Nvidia GPU. It is good and recommended for better performance. It needs to Install/Update nvidia driver, cuda toolkit, cuDNN and then run following command to install

For more information, check out the official guide here.
Jupyter Notebook Visual Studio Code No Kernel

The next is to install Matplotlib- a Python library for 2D plotting and can work together with NumPy.
3. Install Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is web based interactive environment for writing the code, creating & sharing files and doing visualizations as well.
run following command to install it:
Start the notebook server from the command line:
You should see the notebook open in your browser.
If you want to specify port:
4. Setup VS Code
Download and install VS Code if not already installed.
Install the following VS Code extension from the marketplace.
Note: Make sure you have installed the latest version of the extension.
First time, open the VS Code Command Palette with the shortcut CTRL + SHIFT + P (Windows) or Command + SHIFT + P (macOS) in VSCode and select “Python: Select Interpreter” command. It will display all installed versions. Select the appropriate python environment where Jupyter notebook is installed.
To create new Jupyter notebook, open VS Code Command Palette again and run the “Python: Create Blank New Jupyter Notebook” command.
Why VS Code?
– You can manage source control, open multiple files, and leverage productivity features like IntelliSense, Git integration, and multi-file management, offering a brand-new way for data scientists and developers to experiment and work with data efficiently.
– Variable Explorer will help you keep track of the current state of your notebook variables at a glance, in real-time.
– You can export as Python code and do debugging and other operation like do in regular python application
5. Testing Environment
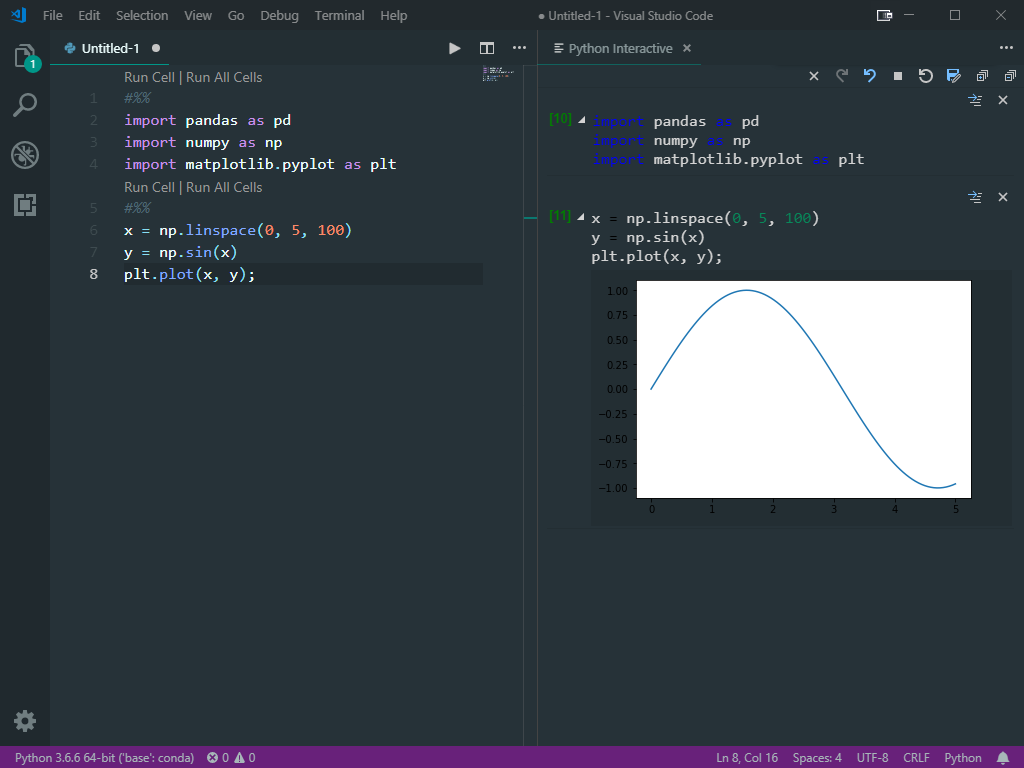
Now, it is time to test the environment.
Create a new Jupyter book in VS Code and run following code to test :
The output should be following:
6. Virtual Environment (Optional)
a) As we are going to use same environment for all so installed TensorFlow, Jupyter Notebook in global Python environment. If you want to create a separate environment for this, you can create a virtual environment by running following command:
It will create .venv directory at specified path.
b) To activate python virutal environment
In VS Code:
In Command Palette CTRL + SHIFT + P, Run “Python: Create Terminal“. It will open and activate the terminal in selected Python environment.
c) Now install the TensorFlow, Jupyter notebook …etc in the activated environment.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we saw
– how to set up a Python Deep Learning development environment using TensorFlow 2.0, Jupyter Notebook and VS Code.
– how Python extension in VS Code empowers notebook development in developer way.
If you face any problems, then feel free to share them in the comment section.
Enjoy Deep Learning !!
-->Important
On January 15, 2021 the Azure Notebooks public preview site retired and has been replaced with integrated services from Visual Studio, Azure, and GitHub. To create new or execute notebook content, learn more about our other notebooks experiences from Microsoft.
In this quickstart, you will learn how to import a Jupyter Notebook for use in assorted Microsoft offerings.
If you have existing Jupyter Notebooks or want to start a new project, you can use them with many of Microsoft's offerings. Some options described in the sections below include:
Create an environment for notebooks
If you'd like to create an environment that matches that of the retired Azure Notebooks Preview, you can use the script file provided in GitHub.
- Navigate to the Azure Notebooks GitHub repository or directly access the environment folder.
- From a command prompt, navigate to the directory you want to use for your projects.
- Download the environment folder contents and follow the README instructions to install the Azure Notebooks package dependencies.
Use Notebooks in Visual Studio Code
VS Code is a free code editor that you can use locally or connected to remote compute. Combined with the Python extension, it offers a full environment for Python development including a rich native experience for working with Jupyter Notebooks.
If you have existing project files or would like to create a new notebook, you can use VS Code! For guidance on using VS Code with Jupyter Notebooks, see the Working with Jupyter Notebooks in Visual Studio Code and Data Science in Visual Studio Code tutorials.
You can also use the Azure Notebooks environment script with Visual Studio Code to create an environment that matches the Azure Notebooks Preview.
Use Notebooks in GitHub Codespaces
GitHub Codespaces provides cloud hosted environments where you can edit your notebooks using Visual Studio Code or in your web browser. It offers the same great Jupyter experience as VS Code, but without needing to install anything on your device. If you don’t want to set up a local environment and prefer a cloud-backed solution, then creating a codespace is a great option. To get started:
- (Optional) Gather any project files you would like to use with GitHub Codespaces.
- Create a GitHub repository for storing your notebooks.
- Add your files to the repository.
Use Notebooks with Azure Machine Learning
Jupyter Notebook Vs Visual Studio Code
Azure Machine Learning provides an end-to-end machine learning platform to enable users to build and deploy models faster on Azure. Azure ML allows you to run Jupyter Notebooks on a VM or a shared cluster computing environment. If you are in need of a cloud-based solution for your ML workload with experiment tracking, dataset management, and more, we recommend Azure Machine Learning. To get started with Azure ML:
(Optional) Gather any project files you would like to use with Azure ML.
Create a Workspace in the Azure portal.
Open the Azure Studio (preview).
Using the left-side navigation bar, select Notebooks.
Click on the Upload files button and upload the project files.
For additional information about Azure ML and running Jupyter Notebooks, you can review the documentation or try the Intro to Machine Learning module on Microsoft Learn.
Use Azure Lab Services
Azure Lab Services allow educators to easily setup and provide on-demand access to preconfigured VMs for an entire classroom. If you're looking for a way to work with Jupyter Notebooks and cloud compute in a tailored classroom environment, Lab Services is a great option.
If you have existing project files or would like to create a new notebook, you can use Azure Lab Services. For guidance about setting up a lab, see Set up a lab to teach data science with Python and Jupyter Notebooks
Use GitHub
GitHub provides a free, source-control-backed way to store notebooks (and other files), share your notebooks with others, and work collaboratively. If you’re looking for a way to share your projects and collaborate with others, GitHub is a great option and can be combined with GitHub Codespaces for a great development experience. To get started with GitHub
- (Optional) Gather any project files you would like to use with GitHub.
- Create a GitHub repository for storing your notebooks.
- Add your files to the repository.
Next steps
